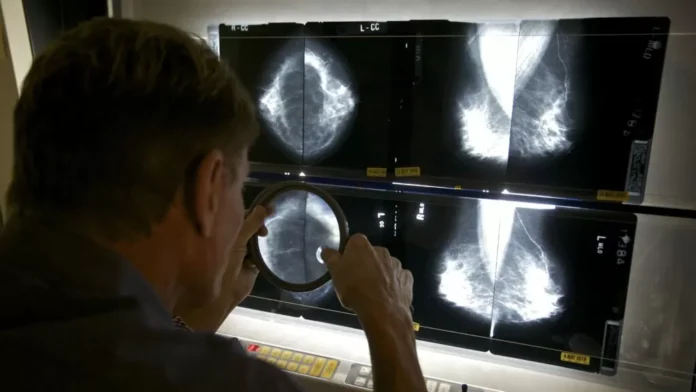
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been a hot topic in the medical field, with its potential to revolutionize the way we detect and diagnose diseases. One area where AI is showing great promise is in radiology, where it can assist radiologists in spotting abnormalities in medical images.
Traditionally, radiologists have relied on their expertise and visual interpretation of medical images to identify diseases. However, this process can be time-consuming and prone to human error. With the help of AI, radiologists can now analyze and interpret large volumes of medical images in a fraction of the time, allowing for quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
For instance, AI-powered screenings have been particularly successful in detecting breast cancer in mammograms. A study conducted by Google Health showed that AI was able to identify breast cancer with a 99% accuracy rate, compared to 96% accuracy for human radiologists. This is a significant improvement that has the potential to save thousands of lives.
Moreover, AI screenings can also assist in detecting other types of cancer, such as lung cancer, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. By analyzing CT scans of the lungs, AI can identify suspicious nodules that may indicate the presence of cancer. This allows for early detection and treatment, which can significantly improve a patient’s chances of survival.
While the potential of AI in radiology is undeniably promising, it is important to acknowledge that there are risks involved in utilizing this technology on a large scale. One of the main concerns is the possibility of false-positive or false-negative results. This means that the AI system may identify a healthy patient as having a disease, or vice versa. This could lead to unnecessary follow-up tests and procedures, causing anxiety and financial burden for the patient.
Additionally, there is also a risk of overreliance on AI by radiologists. With the technology doing most of the work, there is a chance that radiologists may become complacent and not thoroughly review the results. It is crucial to remember that AI is meant to assist, not replace, the expertise of radiologists.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to have proper protocols in place for the use of AI in radiology. This includes continuous training and evaluation of the AI systems, as well as close collaboration between AI developers and radiologists. It is also crucial to have a human-in-the-loop approach, where radiologists review and confirm the AI-generated results before making a diagnosis.
Moreover, it is essential to have strict regulations and guidelines for the use of AI in healthcare. This will ensure that the technology is used ethically and responsibly, with the best interests of the patients in mind.
Despite these potential risks, the benefits of AI in radiology far outweigh any concerns. The speed and accuracy of AI screenings can significantly improve patient outcomes, especially for life-threatening diseases such as cancer. Furthermore, as AI continues to learn and improve, its accuracy and efficiency will only increase, making it a valuable tool for radiologists.
In conclusion, the potential of AI in radiology is undeniable. It has already shown significant success in detecting diseases, and with proper protocols and regulations in place, it can further improve patient care and outcomes. As with any new technology, there are risks involved, but with responsible implementation, we can harness the power of AI to revolutionize the field of radiology and ultimately, save lives.